The scientific classification of plants and animals - influenced by Charles Darwin - also shaped thinking about beauty. It was seen to be definable, like a plant type or animal species. Increasingly, sophisticated knowledge of medicine and anatomy and the association of beauty with health also saw physicians weigh into the debate.
A look at three significant books that focused on beauty shows several influential ideas. These include the classification of distinct beauty types, the perception of “natural” beauty as superior to the “artificial”, and the eventual acceptance of beauty as something that each woman should try to cultivate through a daily regimen of self-care.
Classifying beauty types
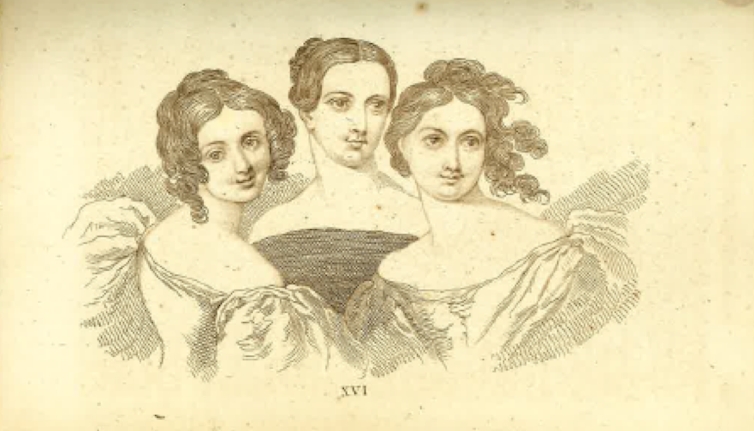 |
| ‘The three species of beauty as affecting the head and face’ in Alexander Walker’s Beauty; Illustrated Chiefly by an Analysis and Classification of Beauty in Woman (New York: William H. Colyer). |
Given that one of its key functions is to signal fertility, a woman’s appearance is therefore not a frivolous topic. It is linked to the development of humanity.
Walker defines three types or “species” of female beauty: locomotive, nutritive, and thinking. These types derive from a knowledge of anatomy and each is related to one of the bodily “systems”.
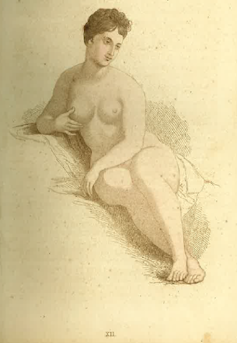 |
| ‘Front view illustrating mental beauty’ in Alexander Walker’s Beauty |
The locomotive or mechanical system is highly developed in women with “precise, striking, and brilliant” bodies. The nutritive or vital system is evident in the “soft and voluptuous”. The thinking or mental system is conducive to a figure “characterised by intellectuality and grace”.
Walker’s ideal is the mental or thinking beauty. She has less pronounced breasts and curves and admirable inner qualities that are evident in her “intensely expressive eye”.
Not coincidentally, he understands intelligence to predominate in men. Walker’s ideal thinking beauty is effectively most like his idea of a man in contrast to the locomotive beauty (connected with the lower classes) and the nutritive beauty (primed to have children).
‘Firm and elastic’ breasts
Daniel Garrison Brinton was an army surgeon in the American Civil War. He later became a professor of ethnology and archaeology and edited The Medical and Surgical Reporter. In 1870, he and medical editor George Henry Napheys published Personal Beauty: How to Cultivate and Preserve it in Accordance with the Laws of Health. The book proposes ideal measurements for areas such as the forehead and the most distinctive features of the female body. Breasts are viewed as essential to beauty and the ideal they describe is youthful, with “firm and elastic” tissue that forms “true hemispheres in shape”.
Very specific distances between nipples, the collar bone, and between the breasts themselves are specified, setting out perfect proportions.
Brinton and Napheys claim that few European and American women meet these requirements, owing to the “artificial life” adopted in both locations. Controversially, they remark that such breasts do not exist in America, apart from in “some vigorous young country girl, who has grown up in ignorance of the arts which thwart nature”. The idea that beauty was more often destroyed by “artificial” beauty methods than improved by it was predominant.
Personal Beauty promotes a device for improving the shape of the breast through suction because it meets the criteria for “natural” improvement. It is described similarly to breast enlargement pumps that are sold today as an alternative to breast augmentation.
Brinton and Napheys’ reference to the potential of such a device to “restore the organs in great measure to their proper shape, size, and function” suggests they are referring to breasts that may have lost their fullness and symmetry after breastfeeding.
It is unclear how such a device would not only improve the shapeliness of breasts, but also render them “better adapted to fulfil their functions”. However, the notion that function, which is reliant on health, is essential to beauty helps to support a medicalised understanding of the topic.
Beauty destroyed
This emphasis on health contributes to a tendency to focus on the ways that women destroy their own beauty through clothing, cosmetics, or certain types of exercise. A specific target in this book is the wearing of garters below the knee, which the authors claim is the reason why a “handsome leg is a rarity, we had almost said an impossibility, among American women”. Tightly-laced corsets, sucked-upon lips, and white face powders are frowned upon for potential harms to health. Yet, as doctors, Brinton and Napheys embrace early manifestations of cosmetic surgery, such as the removal of skin that might hang over the eyes.
A significant point in guiding the acceptability of cosmetic usage is whether such a practice appears natural and undetectable. Imitation itself is not described as distasteful, if it can be achieved convincingly, but “the failure in the attempt at imitation” does inspire revulsion.
As such, a wig that meshes with a women’s age and appearance can be acceptable. In contrast, it is “contrary to all good taste” to “give to the top of the head an air of juvenility which is flatly contradicted by all other parts of the person”.
Personal Beauty focuses on preventative measures for retaining beauty and delaying the visible onset of ageing, rather than remedying flaws once they have taken hold. The book ultimately concludes that if all the measures recommended are undertaken, “there will be little need for the purely venal cosmetic arts, such as paint, powder, patches, or rouge”.
Embracing beauty culture
This understanding of cosmetics as pure reflections of vanity and as separate from beauty practices related to health was gradually challenged by women writers towards the end of the 19th century.  |
| Frontispiece, Mrs H.R. Haweis, [1878] 1883. The Art of Beauty. London: Chatto & Windus. |
Eliza Haweis wrote about the decoration and stylistic adornment of the home and body in British magazines and a series of books, the first of which was The Art of Beauty (1878). Its premise is that personal beauty and adornment of the body is of “the first interest and importance” for women.
Many beauty manuals warned against any significant attempts to alter the face or body beyond basic health and hygiene. Such practices, as academic Sarah Lennox suggests, were seen as “objectionable — as a hiding of inner truth”. Haweis, however, encourages young women to enhance their beauty and older women to continue to use methods that “conceal its fading away”.
The methods that Haweis advocates reproduce prevalent ideas found in women’s magazines and beauty manuals that discouraged any visible sign of artifice and which championed the “natural”. Hygienic and cosmetic intervention are framed as exposing or fostering physical qualities as they ought to be seen, or providing a delicate “veil” for flaws, rather than attempting to entirely transform them.
However, Haweis goes further than many beauty advisors at the time. Unlike many male writers, she is not opposed to cosmetics. She likens their use in “hiding defects of complexion, or touching the face with pink or white” to adding padding to a dress, piercing ears, or undergoing cosmetic dentistry.
 |
| Eliza Haweis |
Haweis, however, is unique in her entertainment of the possibility of ugliness negatively influencing character. She proposes that “an immense number of ill-tempered ugly women are ill-tempered because they are ugly”. She acknowledges that ugliness is in fact an “impediment” and a “burden”, which thereby supports her call to all women to work to improve their appearance.
Beauty today
Our understanding of what makes a woman beautiful is influenced by dominant cultural beliefs and hierarchies. Though Walker’s physiological beauty types were replaced by acceptance of the idea that women can retain beauty into older age or remedy unappealing features, many historic precepts about beauty continue to influence modern beauty culture. Ideas about “natural” beauty as superior to “artificial” beauty are reflected in cosmetic advertisements and plastic surgery procedures, with a “natural” or “undetectable” look to any product, facelift, or implant being the desired outcome for many women.
Most of all, the idea that beauty is of prime importance to girls and women remains predominant, even as the cultural conditions surrounding marriage, employment, and family have substantially transformed since the 19th century.
Haweis’ ideas about the significance of self-care resonate with contemporary feminists who point to women’s pleasure and empowered use of cosmetics.
We have recently seen the emergence of male beauty bloggers and YouTubers. However, the continued sense that beauty is largely women’s preserve and a unique form of power that requires a continual fight to keep shows how an emphasis on women’s physical appearance is still entwined with gender inequality.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




